In 2022, cyber criminals have sent about 3.3 billion phishing messages and caused over 4000 data breaches. This exposed about 22 billion personal records.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a cybercrime in which a target or targets are contacted by email, telephone or text message by someone posing as a legit institution to lure individuals into providing sensitive info. And such as PII banking and credit card details and passwords. The information is then used to access important accounts and can result in identity theft and financial loss.
How do we fight phishing?
Knowledge
Humans are the number one cause of phishing schemes to succeed. So knowledge is definitely going to be one of your big tools. Make your employees knowledgeable about phishing attacks, the common phishing attacks that are happening now and answer any questions that they might have about these different security issues.
Safeguards
Over 50% of the attacks were caused by humans, but that other 40 something percent was caused by issues in the system. So having safeguards in place, such as a really good spam filter, can help fight against phishing.
And what’s interesting is, Google actually has better safeguards in place than Microsoft Office. So organizations that use Office 365, are more than three times as likely to experience a business email compromise when compared to Google Gmail for business.
One reason that’s probably true is because Microsoft only has access to their small amount of data that is Microsoft specific, whereas Google has access to 90% of the world’s data on the internet. So it would make sense that the Google spam filter and their email filters are much, much stronger, because they have access to so much more data.
Ways to spot phishing schemes
It contains an offer, that’s, that’s too good to be true
If you’ve ever received an email that said “click here to claim your $500 reward”, they want you to go to a website and put in your name and your bank account so they can deposit that $500 reward.
Language that’s urgent, alarming or threatening
In one week, we had three different clients send an email that says the subject line is urgent, your site has been hacked. And the email goes on to say, deliver $3,000 in Bitcoin, or we will take your website offline, and put something else up in its place. So anytime you receive anything like that, that’s definitely a big key to spotting phishing.
Poorly crafted writing with misspellings and bad grammar
Now, this next one, it’s not as prevalent anymore with AI becoming a lot more in tune. More of, you know, chat, GBT, stuff like that. You and I know that no financial institution and no attorney is going to send out anything that has bad grammar. So that’s definitely a way to spot a phishing email.
Greetings that are ambiguous or very generic
You may receive an email that says hello gentleman, or welcome lady. Ignore these.
Requests to send personal information.
This happens a lot with people pretending to be banks, or pretending to be PayPal. They’ll say, oh, there’s an issue with your account, click here to sign in and put in your financial information so we can verify it. Don’t do that. PayPal and banks have come out and said, we will never send you an email that’s like that, so that’s definitely an email to ignore.
Urgency to click on unfamiliar hyperlinks or an attachment
A real website for a bank, credit card company, or other business won’t look or feel like it’s trying too hard. You won’t find important messages spread all over these sites. If you go to a site and it seems to have a lot of urgent messages that don’t seem to fit, you should check the URL to make sure you’re in the right place. Phishers use this kind of urgency to make it more likely that people will share sensitive information quickly and willingly.
Strange or erupt business requests
In this type of phishing attack, the victim is sent an email from an address they know, like the CEO, the Human Resources Manager, or the IT support department. The email tells the victim that they need to act quickly and transfer money, update information about their employees, or install a new app on their computer.
Fuzzy or low resolution images
A company will never send you an email where their logo looks bad. If their logo looks bad or fuzzy, whoever sent it didn’t have access to the high resolution version of it. So it’s not from them.
The sending email address doesn’t match the company where it’s coming from
So if they say, Hi, this is PayPal, but the address says PayPal1234@outlook.com, those two don’t mesh. And so, you know it’s not from PayPal.
What does a phishing email look like?
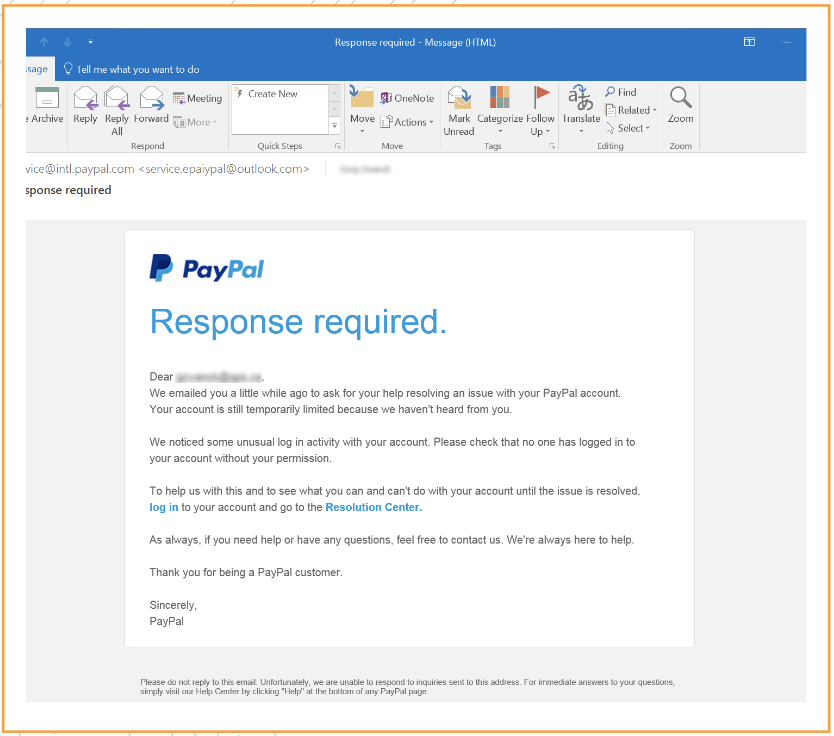
As an example, we have this email where you can see this isn’t the actual PayPal logo, it’s a little bit different. It’s missing a few features. And then it says response required. Then you can see here it says service.epaypal@outlook.com. The purpose of this email is they want you to click this login and put in your username and password, so they have your paypal username and password.
Common phishing schemes
Account deactivation
Compromised credit card
Funds Transfer
Social media requests
Google Docs fake login
IT support request
Social engineering
Questions about anything in this article? Contact Stacey Ivol at 412-563-2106 or email her at sivol@integrityfirstins.biz
